
Service hotline:
13533607738
18602592233
Welcome to 广东脊祥万岁健康管理有限公司!
最新资讯
Muscular atrophy Myatrophy (myophagism) refers to the reduction of muscle volume caused by rhabdomyodystrophy, thinning or even disappearance of muscle fibers. Muscle diseases or nervous system dysfunction are the main causes: neurogenic muscle atrophy, myogenic muscle atrophy, disused muscle atrophy and other causes of muscle atrophy. Muscle nutrition is closely related to nervous system besides the pathological changes of muscle tissue itself. Spinal cord disease often results in muscular dystrophy and muscle atrophy. Muscle atrophy patients are bedridden for a long time due to muscle atrophy and muscle weakness, and are prone to pneumonia and pressure sores. In addition, most patients suffer from bulbar palsy, which poses a great threat to their lives.
Can it recover from atrophy?
1.Neurogenic muscular atrophy
Common causes are waste, nutritional disorders, ischemia and poisoning. Anterior horn lesions, nerve root, nerve plexus, peripheral nerve lesions can cause nerve excitation impulse conduction disorders, so that some muscle fibers are discarded, resulting in discarded muscle atrophy. On the other hand, when motor neurons are damaged at any part of the brain, acetylcholine released from their terminals decreases, and sympathetic neurotrophic function weakens, resulting in muscle atrophy.
2.Myogenic muscular atrophy
It is caused by muscular disease itself, and may also include other factors, such as shoulder strap or facio-shoulder-brachial muscular dystrophy, which has been confirmed by morphological examination as spinal muscular atrophy. Microelectrode technique was used to examine muscular dystrophy in animals. About 1/3 of them showed functional denervated muscle fibers.
Two main types of factors can cause "muscle atrophy": neurogenic muscle atrophy is called neurogenic muscle atrophy after nerve injury, and myogenic muscle atrophy is called muscle disease itself.
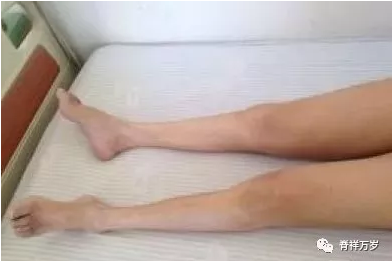
Clinical manifestation
1Thigh muscle atrophy
Quadriceps femoris atrophy is the main cause. Thigh muscle atrophy is common in femoral head necrosis patients and lower limb brake patients. All patients with femoral head necrosis have thigh muscle atrophy in the middle and late stages. The severity of muscle atrophy is different. Most of the disused thigh muscle atrophy can be restored. In a few cases of femoral head necrosis, thigh muscle atrophy can not be restored for life. Influencing walking distance and quality of life of patients。
2Muscle atrophy of calf
It refers to rhabdomyodystrophy, muscle volume is smaller than normal, muscle fibers become thinner or even disappear.
3Muscle atrophy of scapular band
It is the symptom and clinical manifestation of progressive proximal muscular atrophy of extremities. Progressive proximal muscle atrophy of extremities is usually myogenic atrophy. The proximal and trunk muscles of extremities are obvious. It is often manifested by the atrophy and weakness of scapular and pelvic muscles.
4Myogenic facial muscular atrophy
It is caused by muscular disease itself, and may also include other factors, such as shoulder strap or facio-shoulder-brachial muscular dystrophy, which has been confirmed by morphological examination as spinal muscular atrophy. On the other hand, when motor neurons are damaged at any part of the brain, acetylcholine released from their terminals decreases, and sympathetic neurotrophic function weakens, resulting in muscle atrophy.
5Atrophy of interosseous and thenar muscles
Usually small muscle weakness and muscle atrophy of the hand begin to affect one side or both sides, or from one side to the other. The palms are flat due to thenar muscle atrophy and claw-like hand due to interosseous muscle atrophy. Muscle atrophy extends upward and gradually invades the forearm, upper arm and shoulder strap. Muscle fascicular fibrillation is common and can be limited to some muscle groups or widespread. It is easy to induce by hand beating. A small number of muscular atrophy weakness can start from the tibialis anterior and fibula muscles of the lower extremities or from the extensor of the neck, or from the proximal muscles of the upper and lower extremities.
6Classification of muscular atrophy and muscle strength
(1)Level 0: Completely paralyzed, unable to do anything free and powerless.
(2)Grade I: Complete paralysis, slight muscle atrophy can be seen during limb movement, but the body can not move.
(3)Class II: Limbs can move parallel on the bed, but not off the bed.
(4)Level III: Limbs can overcome the gravitational attraction and lift off the table.
(5)Class IV: Limbs can move against external resistance.
(6)Grade V: Normal muscle strength and free movement.
inspect
1. Electromyography (EMG).
2. Nerve conduction velocity, including motor nerve conduction velocity, sensory nerve conduction velocity, F wave and H reflex.
3. Evoked potentials, including brainstem auditory evoked potentials, visual evoked potentials and upper and lower limb somatosensory evoked potentials.
4. Examination of bare-handed muscle strength.
5. Muscle tension test.
6. Measurement of muscle circumference.
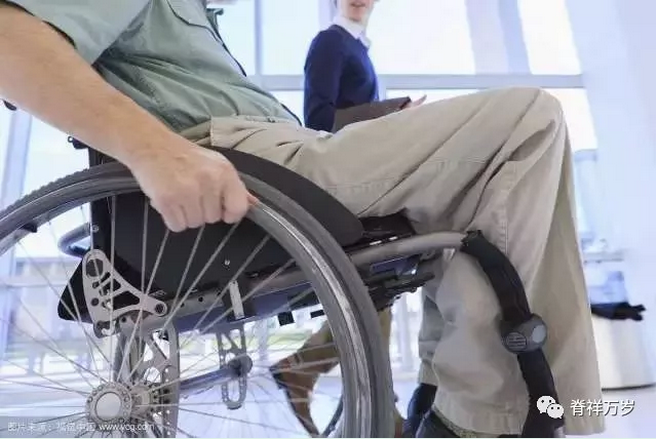

Treatment
01
Patients with Limb Dyskinesia caused by muscle atrophy can significantly reduce or alleviate the sequelae of paralysis after regular exercise therapy.
Some people mistakenly regard sports therapy as particularly simple, even equate it with "exercise", eager to achieve, often with half the effort, and lead to joint muscle injury, fracture, shoulder and hip pain, aggravation of spasm, abnormal spastic pattern and abnormal gait, as well as foot drop, varus and other issues, namely "misuse syndrome".
We should not neglect the coordinated rehabilitation therapy among the range of motion, muscle tension and antagonism of the patients, so as to avoid the patients'muscle strength returning to normal, but leaving behind abnormal movement patterns.
02
The inappropriate muscle strength training can aggravate the spasm, and the appropriate rehabilitation training can alleviate the spasm, so that the limb movement tends to be coordinated. Once the wrong training methods are used, such as gripping with the affected side's hands repeatedly, it will strengthen the flexor coordination of the affected side's upper limbs, aggravate the muscle spasm responsible for joint flexion, cause elbow flexion, wrist flexion, finger flexion deformity, and make the recovery of hand function more difficult. In fact, dyskinesia of muscular atrophy limbs is not only a problem of muscle weakness, but also an important cause of dyskinesia. Therefore, we should not mistake rehabilitation training as strength training.
03
Low or medium frequency stimulation, neurotrophic drugs, combined with acupuncture/electroacupuncture and massage
Self regulation
Besides consulting a doctor for treatment, self-regulation is very important for patients with muscular atrophy.
1.Keep optimistic and happy
Strong long-term or repeated emotional changes such as stress, anxiety, irritability and pessimism can imbalance the excitation and inhibition process of cerebral cortex and promote the development of muscular atrophy.
2.Rational allocation of dietary structure
Muscular atrophy patients need high-protein and high-energy diet supplements, which provide the necessary substances for the reconstruction of nerve cells and skeletal muscle cells to enhance muscle strength and muscle growth. Early use of high-protein, rich in vitamins, phospholipids and trace elements of food, and actively cooperate with Qi-invigorating and spleen-invigorating medicinal diets, such as yam, astragalus, white lotus, tangerine peel, Radix pseudostellariae, Lily and so on, fasting spicy food. Stop smoking and drinking. In the middle and late stages, high protein, high nutrition, energy-rich semi-liquid food and liquid food were the main foods, and fewer meals and more meals were used to maintain the balance of nutrition and water and electrolytes.
3.Strike a proper balance between work and rest
Avoid forced functional exercise, because forced functional exercise will cause fatigue of skeletal muscle, which is not conducive to the recovery of skeletal muscle function, the regeneration and repair of muscle cells.
4.Prevention of colds and gastroenteritis
Muscular atrophy patients are prone to pulmonary infection because of their low autoimmune function or some kind of immune deficiency. Once they catch a cold, their condition becomes worse, the course of disease prolongs, muscular weakness and muscle jump aggravates. Especially, patients with bulbar paralysis are prone to pulmonary infection. If not prevented and treated in time, the prognosis is poor and even endangers the lives of patients. Gastroenteritis can lead to intestinal bacterial dysfunction, especially viral gastroenteritis has different degrees of damage to anterior horn cells of spinal cord, so that the condition of muscular atrophy is repeated or aggravated. Maintaining normal digestive function in patients with muscular atrophy is the basis of rehabilitation.